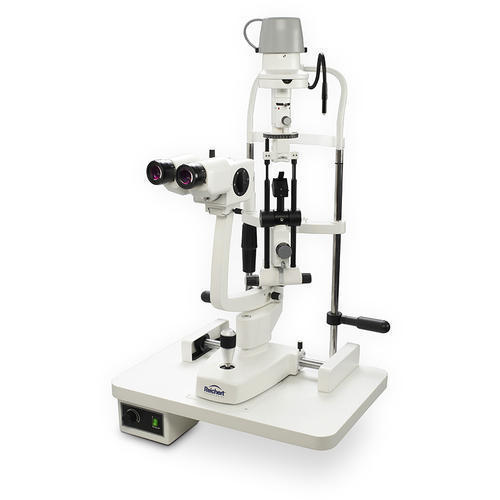
ConXport . Slit Lamp (Ultima) Stepper Magnification (5 Steps)
ConXport . Slit Lamp (Ultima) Stepper Magnification (5 Steps) Specification
- Core Components
- Optical Lenses, Stepper Magnification System
- Accuracy
- High Precision Optical System
- Automation Grade
- Manual
- Power Source
- Electric
- Feature
- 5-Step Magnification (6x, 10x, 16x, 25x, 40x), High Resolution
- Voltage
- 220V AC
- Model No
- Ultima
- Measurement Range
- Magnification 6x, 10x, 16x, 25x, 40x
- Frequency
- 50 Hz
- Equipment Materials
- Aluminum Alloy, Stainless Steel
- Type
- Stepper Magnification Slit Lamp
- Usage
- Ophthalmic Examination
- Display Type
- Optical
- Dimension (L*W*H)
- 600 x 300 x 700 mm
- Weight
- Approx. 11 kg
ConXport . Slit Lamp (Ultima) Stepper Magnification (5 Steps) Trade Information
- FOB Port
- Delhi
- Payment Terms
- Letter of Credit (L/C), Paypal, Telegraphic Transfer (T/T)
- Supply Ability
- 15 Per Week
- Delivery Time
- 6-7 Days
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- If order is confirmed we will reimburse the sample cost
- Main Export Market(s)
- Australia, North America, South America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Middle East, Africa, Central America, Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
- Certifications
- ISO,CE,FDA,WHO-GMP
About ConXport . Slit Lamp (Ultima) Stepper Magnification (5 Steps)
Details
Slit Lamps - 4 Models
The slit lamp is essentially a simple and generally under-used piece ofequipment. It consists of an illumination system and a binocular observationsystem, which when correctly aligned will result in a coincidental focus of theslit and microscope.
Illumination system
Basically a short focus projector projecting an image of the illuminated slitaperture on to the eye. This part of the system should be flexible to allowvarious sizes and shape of slit beam. Usually a rheostat is incorporated andthe lamp house can be rotated. Neutral density, cobalt blue and red freefilters are usually available, and occasionally a diffuser and polarizer
Using the slit lamp
Commence the examination using the 10x eyepieces and the lower poweredobjective i.e. 1x. Use the lowest voltage setting on the transformer. Selectthe longest slit length by means of the appropriate lever (17). Adjust the chinrest by means of control 27 so that the patients eyes are approximately levelwith the black marker on the side of the head rest. Adjust the height of theslit lamp until the slit beam is centred vertically on the patients eye. Focusthe slit beam on the eye by moving the joystick (1) either towards or away fromthe patient. Coarse positioning can be effected without using the microscopebut critical focussing should be carried out whilst viewing through themicroscope. The slit width is varied by rotating either the left hand or righthand knurled control 10. To vary the angle between illumination and microscopeuse one or other of these same controls as handles.
The slit should be set primarily in the vertical position, butany desired inclination can be achieved by means of the ball handle 15 (notchesat 45, 90, 135; stops at 0 and 180). By tripping the latch 11 and tiltingthe slit lamp column, the beam can be introduced from as much as 20 below thehorizontal. This is mainly used for carrying out gonioscopy.
For observation by sclerotic scatter or other dissociated formsof examination the centering screw 13 is loosened, so that the slit image canbe moved away from the centre of the field of observation. The image iscentered again by tightening the screw. Carry out the techniques describedbelow.
|
Specifications - Binocular Microscope |
|||
|
|
Viewing Oculars |
: |
Binocular, Galilean Type |
|
|
Magnification Change |
: |
Five Steps Drum Rotation Tyte Magnification |
|
|
Eye Pieces |
: |
Wide Field 12.5X |
|
|
Objective |
: |
0.4x, 0.6x, 1x, 1.6x, 2.5x |
|
|
Total Magnification |
: |
5x, 7.5x, 12.5x, 20x, 30x |
|
Illumination Unit |
|||
|
|
Slit Image Rotation |
: |
0 to 180 |
|
|
Tilting Illumination |
: |
5 to 20 |
|
|
Filter Disc |
: |
Cobalt Filter, Red Free, Yellow Filter Natural Density and Open Aperture Diaphragm For Infinitely Variable Slit Lengths. |
|
|
Slit Disphragm Disc |
: |
Six Apertures Of 12, 9, 7, 3 and 0.2mm and a Wedge Shaped Diaphragm Of Infinitely Variable Slit Lengths |
|
|
Halogen Lamp |
: |
12 Volt 50 Watts |
Advanced Stepper Magnification System
Equipped with a five-step magnification mechanism, the ConXport Slit Lamp (Ultima) lets clinicians seamlessly switch between 6x, 10x, 16x, 25x, and 40x magnification. This flexibility supports comprehensive eye examinations, allowing for detailed observation of ocular tissues. The 12.5x wide field eyepieces combined with high-grade optical glass ensure exceptional clarity.
Customizable Viewing and Patient Comfort
The slit lamp offers adjustable slit width (014 mm), length (114 mm), and rotation (0180), supporting a wide variety of ophthalmic procedures. Interpupillary and pupil distances are easily adapted for individual users, while the chin rest adjusts up to 70 mm for patient comfort. Smooth base movements allow precise positioning during exams.
Precision Illumination and Durability
With energy-efficient 3W LED illumination and multiple built-in filters (Cobalt Blue, Red-Free, Heat Absorbing, ND), this slit lamp delivers clear, well-lighted images for both routine and specialized analysis. Manufactured from robust aluminum alloy and stainless steel, it promises long-lasting performance in demanding clinical settings.
FAQs of ConXport . Slit Lamp (Ultima) Stepper Magnification (5 Steps):
Q: How does the stepper magnification system benefit ophthalmic examinations?
A: The five-step magnification (6x, 10x, 16x, 25x, 40x) allows clinicians to easily adjust viewing levels, enabling detailed observation of different eye structures and pathologies within one device. This flexibility improves diagnostic accuracy and efficiency during routine or complex examinations.Q: What is the process for adjusting the slit width and length?
A: The slit width (0 to 14 mm) and slit length (1 to 14 mm) can be continuously adjusted using dedicated control knobs. This allows users to tailor the size and shape of the slit beam to suit the specific examination requirement, enhancing visualization of particular ocular features.Q: When should different filters be used during an eye examination?
A: The built-in filters, including Cobalt Blue, Red-Free, Heat Absorbing, and ND, are selected based on the examination needs. For example, the Cobalt Blue filter is essential for fluorescein staining in corneal assessments, while the Red-Free filter helps enhance contrast for retinal nerve fiber evaluation.Q: Where is the ConXport Slit Lamp (Ultima) typically used?
A: This slit lamp is widely utilized in eye clinics, hospitals, and research laboratories across India and internationally. Its robust construction and high-precision optics make it suitable for both general practice and specialized ophthalmology departments.Q: How is patient comfort ensured during use?
A: Patient comfort is achieved through the adjustable chin rest (up to 70 mm), a customizable interpupillary distance range (50 mm 80 mm), and smooth base movements, ensuring both examiner and patient are well accommodated for accurate and efficient procedures.Q: What materials are used in the construction of this slit lamp?
A: The ConXport Slit Lamp (Ultima) is manufactured with high-quality aluminum alloy and stainless steel, ensuring durability, stability, and resistance to wear and corrosion for extended life in clinical environments.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in ENT And Ophthalmic Instruments Category
ConXport Applanation Tonometer
Type : Applanation Tonometer
Model No : ConXport Applanation Tonometer
Equipment Materials : High Grade Metal and Optical Glass
Feature : Precision Measurement, Compatible with Slit Lamp
Weight : Approx. 1.5 kg
Automation Grade : Manual
ConXport . Slit Lamp Five Step
Type : Five Step Slit Lamp
Model No : ConXport Slit Lamp Five Step
Equipment Materials : Highquality Metal and Optical Glass
Feature : FiveStep Magnification, LED Illumination
Weight : Approx. 12 kg
Automation Grade : Manual
ConXport . I/A, Simcoe Cannulas
Type : Irrigation/Aspiration (I/A) cannula
Model No : ConXport I/A Simcoe Cannula
Equipment Materials : Medical grade stainless steel and polypropylene
Feature : Dualport (Simcoe) design for simultaneous irrigation and aspiration
Weight : Approximately 10 g per cannula
Automation Grade : Manual
ConXport Binocular Loupe 2.5x Hiene German
Type : Binocular Loupe
Model No : ConXport Binocular Loupe 2.5x Hiene German
Equipment Materials : Highquality German optics and lightweight metal frame
Feature : 2.5x magnification, lightweight, clear resolution, ergonomic design
Weight : Approx 55g (without frame)
Automation Grade : Manual

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry